Project facts
Presentation
The main goal of the Saint George on a Bike project (SGoaB), led by the Barcelona Supercomputing Center (BSC), in partnership with the Europeana Foundation is to understand the meaning of images from the past. It aims to improve the quality and quantity of open metadata associated with European Cultural Heritage (CH) imagery. To achieve that goal, SGoaB addresses two challenges:
- To transcribe insights about culture, symbols and centuries of evolving iconographic traditions in a knowledge representation accessible to machine learning and artificial intelligence
- To expand conventional machine learning approaches, centered on image recognition, with the ability to decipher the complex pictorial language that characterises iconographic symbols and sacred imagery.
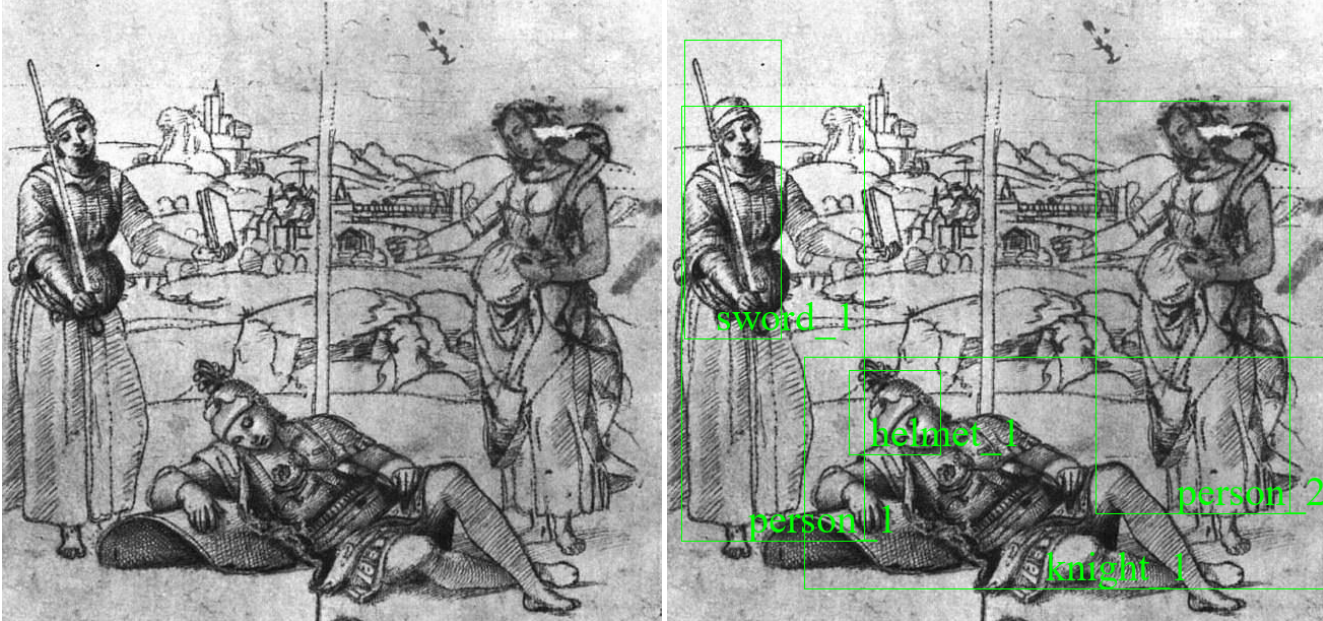
SGoaB relies on deep learning to train object detection and image recognition models, supplemented by natural language processing (NLP) to produce new or enriched image captions. One of its goals is to align image content with the descriptive text, based on both conventional object detection and on the analysis of the image’s pictorial semantics.
Impacts & Results
In spite of a massive worldwide digitization effort of cultural heritage artefacts in recent years, a large portion of online digital collections lacks valuable metadata such as descriptions, captions and other relevant concepts. Attaching a good quality description to every digitized picture should enable all users, including visually impaired people, to better grasp the scope, nature and relevance of a cultural heritage web site’s content. It should empower end-users by making targeted searches for images possible, based on concepts conveyed by the image but not present in its caption; e.g. searching for “pets in 15th century art”.
SGoaB’s goal is to provide a high-performance metadata enrichment capability for the European Data Infrastructure (EUDAT) by using HPC resources in the cultural heritage domain. The objective will be achieved integrating the results of a generic service (AIKON2B) into European Data Infrastructure, specifically as part of the EUDAT Collaborative Data Infrastructure (EUDAT-CDI) metadata store. The use of supercomputing is fundamental for AIKON2B, as the automatic description of images demands the processing of large volumes of data for generating satisfactory quality image descriptions.

